

The House of Representatives Chooses Thomas Jefferson
The presidential election of 1800 ended in a tie, as the two Democratic-Republican candidates, Thomas Jefferson and Aaron Burr, each received 73 electoral votes under the original guidelines of the Constitution.

The End of the Quasi-War
The only fighting in the Quasi-War occurred at sea, and mostly in the Caribbean. But with war at a fever pitch and French interests so close by in Louisiana, there was a very real concern in Congress about a possible French invasion of the United States from the west.

The Whiskey Rebellion
During George Washington’s two terms as President, arguably the most troublesome domestic event was the Whiskey Rebellion. This issue, the root of which was a tax that people refused to pay, threatened the stability of the country. More significantly, the crisis was a direct challenge to the authority of the recently approved Constitution and the federal government which stood behind it.
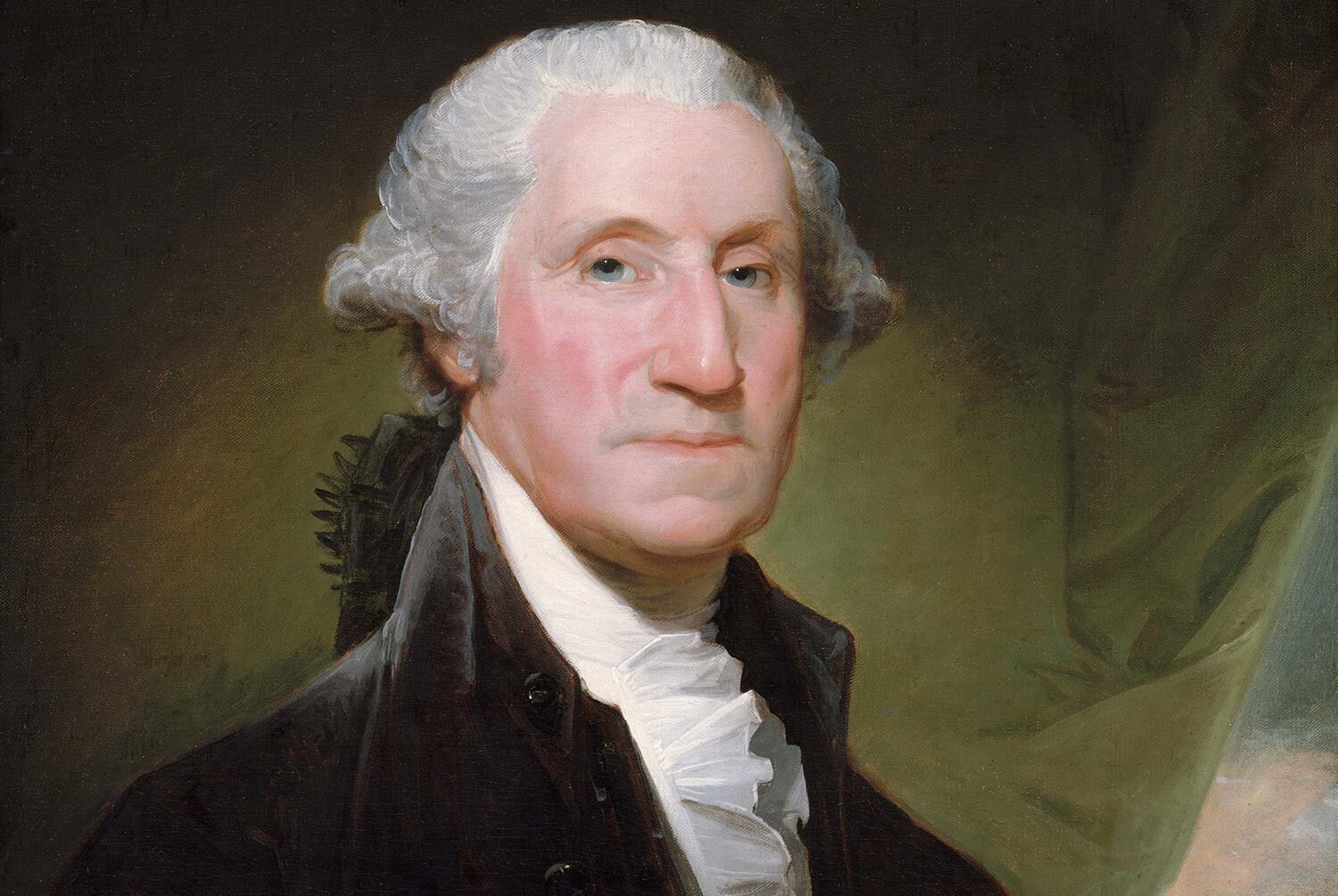

George Washington, Our Nation’s First President
The federal Constitution, the new law of the land, took effect on March 4, 1789, and had several notable differences with the Articles of Confederation. One of the most significant changes was the creation of a strong executive or President. However, the powerful executive reminded skeptics of the authority held by King George, and they worried the United States could eventually drift towards despotism. Virtually everyone knew that the only man strong enough to lead the nation and conscientious enough to be entrusted with so much power was George Washington.

Key Debates at the Constitutional Convention
On May 29, 1787, Edmund Randolph, Governor of Virginia, rose and introduced fifteen resolutions to the Federal Convention. Known to history as the Virginia Resolves or the Virginia Plan, Randolph’s proposal, which was probably drafted by James Madison, was an outline for an entirely new national government. It called for a national executive, a two-house national legislature, and a national judiciary.

The Federal Convention Opens
In the years immediately following the successful conclusion of its war for independence, the United States struggled to survive under the Articles of Confederation. The nation’s leaders knew something had to be done to fix its many issues for this great experiment in democracy to continue.
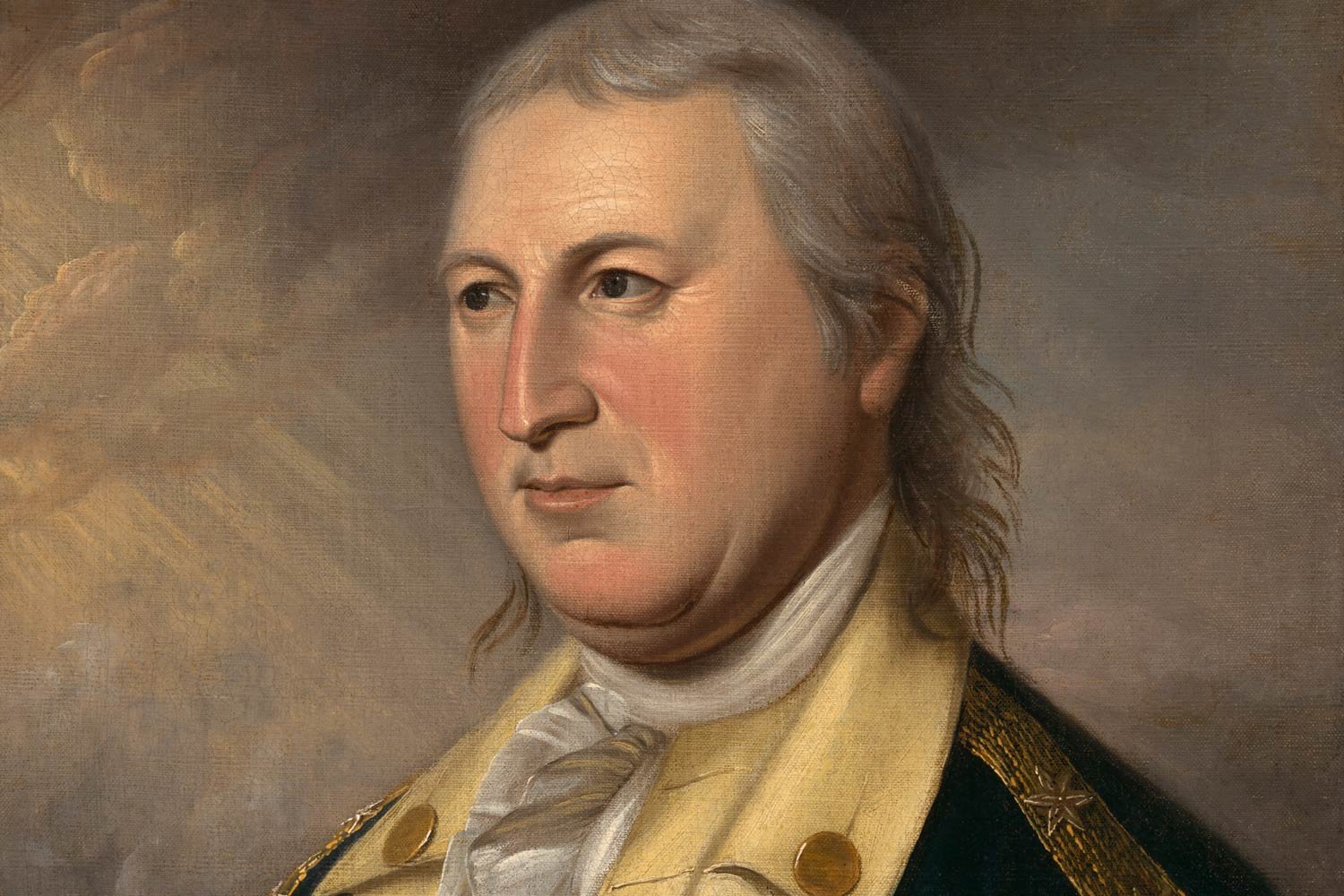

The Newburgh Conspiracy: Washington Ends a Crisis
By early 1783, America was close to finalizing its peace agreement with England. However, the Confederation Congress had some issues to resolve with its own discontented Continental Army, as the internal threat of mutiny appeared worse than the external one posed by British forces.
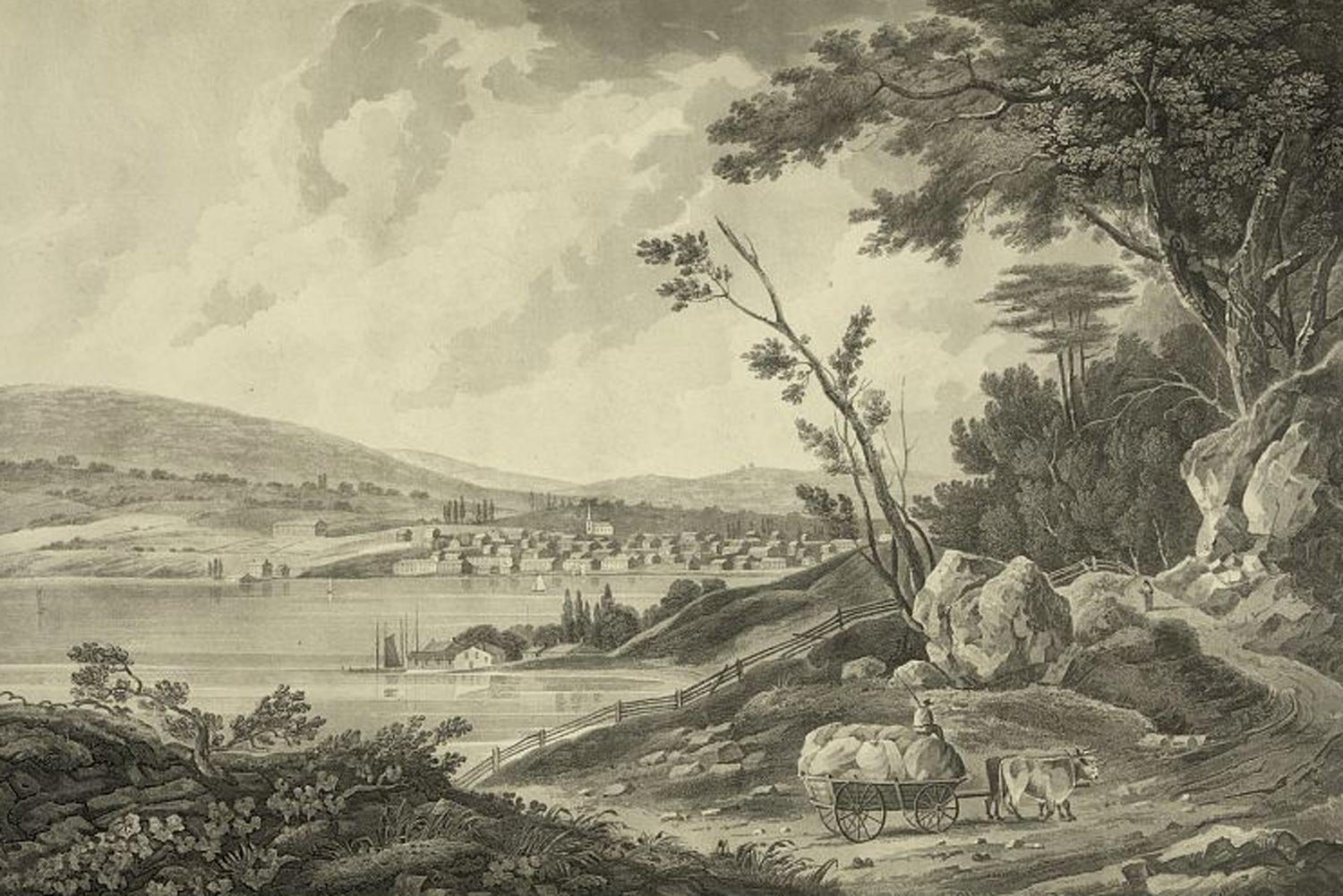

The Newburgh Conspiracy: Dissension in the Ranks
We take civilian control of the military for granted today in America. However, were it not for General George Washington’s actions and words in the so-called Newburgh Conspiracy, things might be quite a bit different.

The Quasi-War and Its Aftermath
The only fighting in the Quasi-War occurred at sea, and mostly in the Caribbean. But with war at a fever pitch and French interests so close by in Louisiana, there was a very real concern in Congress about a possible French invasion of the United States from the west.
Creating the Constitution: Overview
The United States Constitution is arguably the most important legislative document ever written. It has not only shaped our great country, but also influenced many other democracies around the world.




