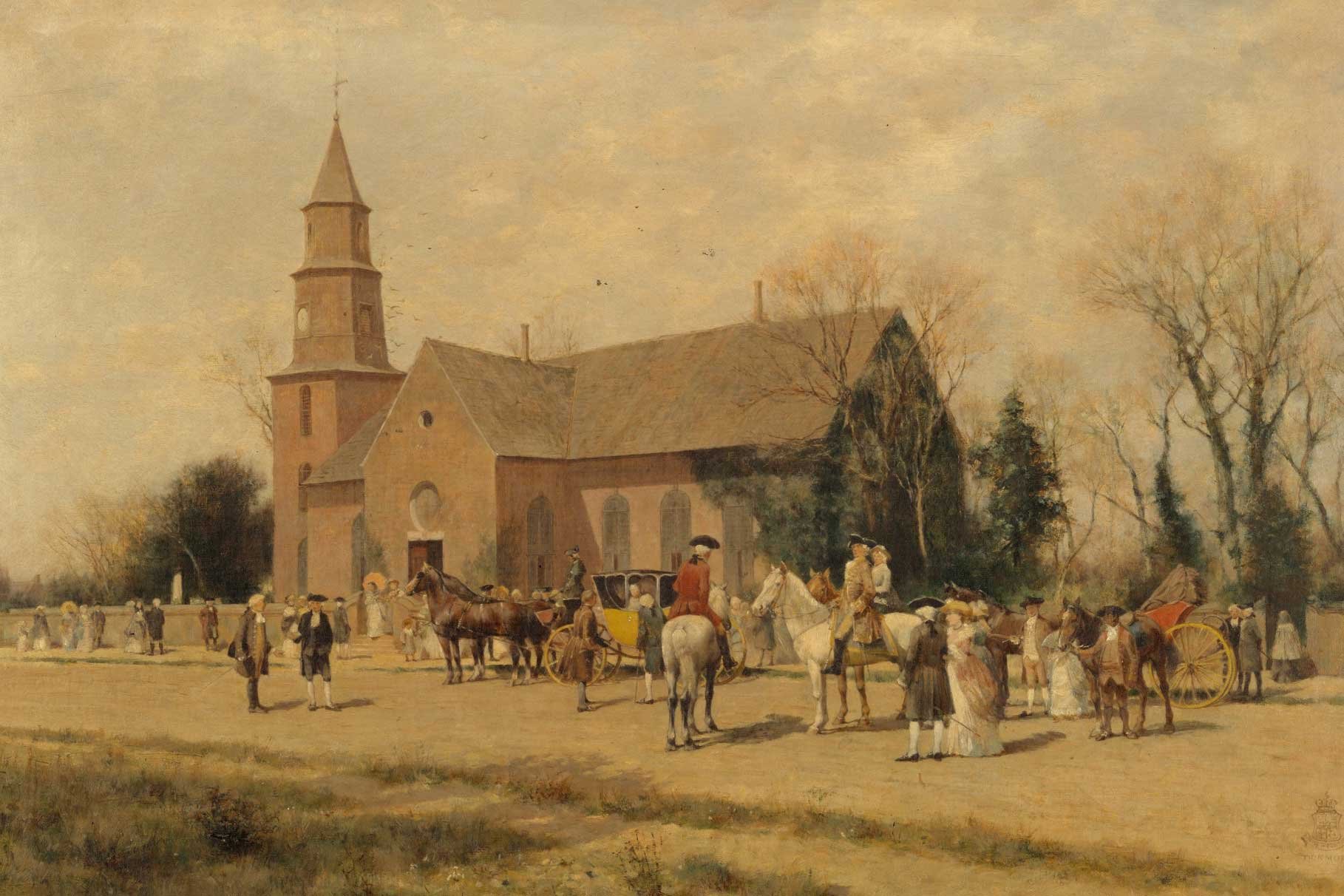
Thomas Jefferson’s “Summary View”
Thomas Jefferson’s revolutionary journey began in the 1760s and culminated in his masterfully written Declaration of Independence in 1776. But in between these events, Jefferson crafted one of the most impactful statements ever for American independence. Entitled A Summary View of the Rights of British America, it was perhaps the most logical assessment of the true relationship between Great Britain and her American colonies. The concepts Jefferson laid out had been refined and brought into focus following several dustups with Lord Dunmore, the new Royal Governor.

Thomas Jefferson, the Virginia Barrister
In 1765, Parliament passed the Stamp Act, the first internal tax on the American colonies, and thus began a decade of missteps by the British. Their miscalculations would take their country and their colonists on a direct path to Lexington Green and Concord Bridge on April 19, 1775. During this same year, Thomas Jefferson was concluding his time studying law under George Wythe and began to turn his eye towards the world at large and, more specifically, politics in the Colony of Virginia.
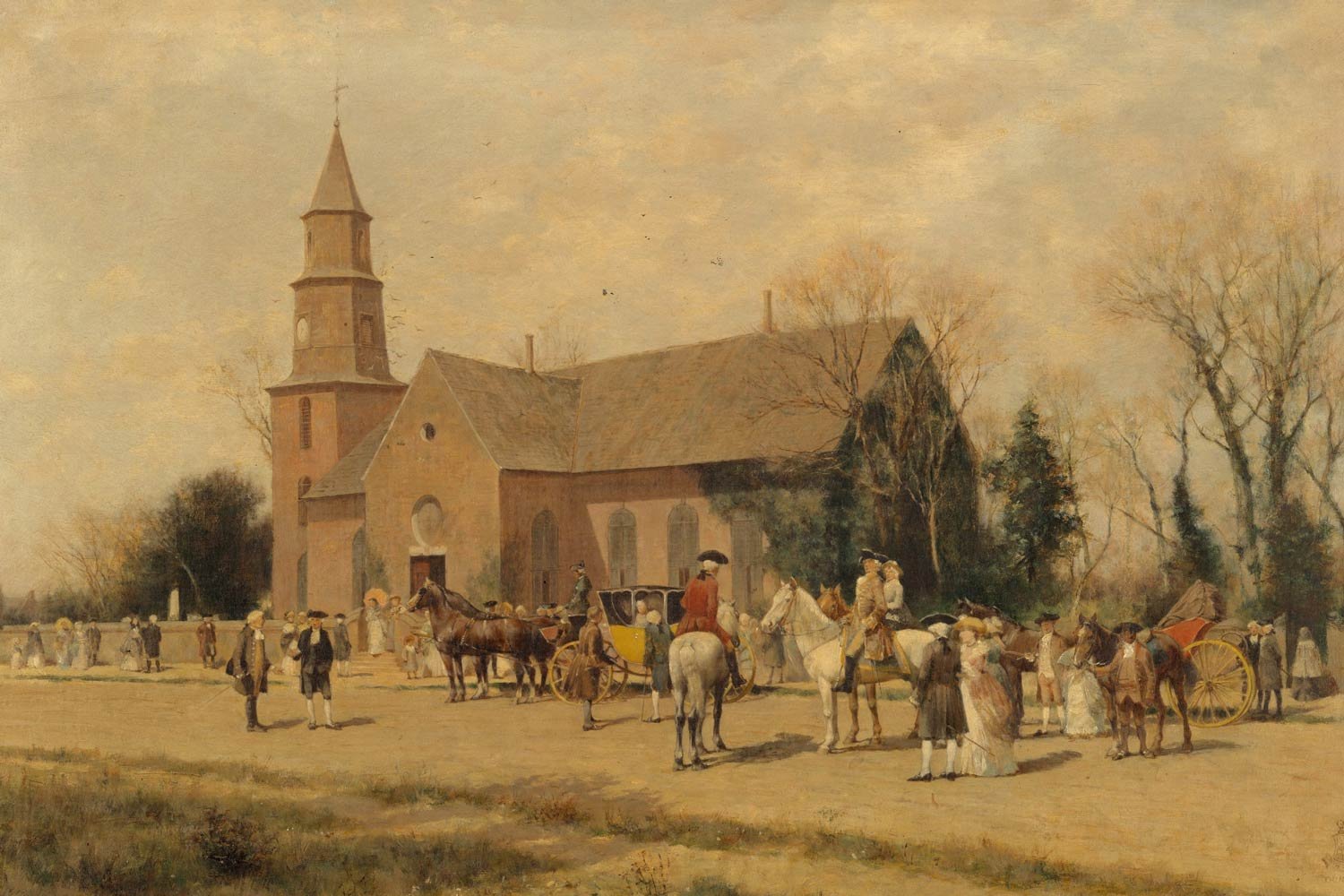
George Washington Enters Politics
As befitting a wealthy landowner in colonial Virginia, George Washington became active in the colony’s politics in the 1750s. He first ran for a seat representing Frederick County in the Virginia House of Burgesses in 1755 but lost the election. Interestingly, it was the only political race he would ever lose. Washington ran for that same seat in 1758 and was victorious, and he held this seat for seven years.
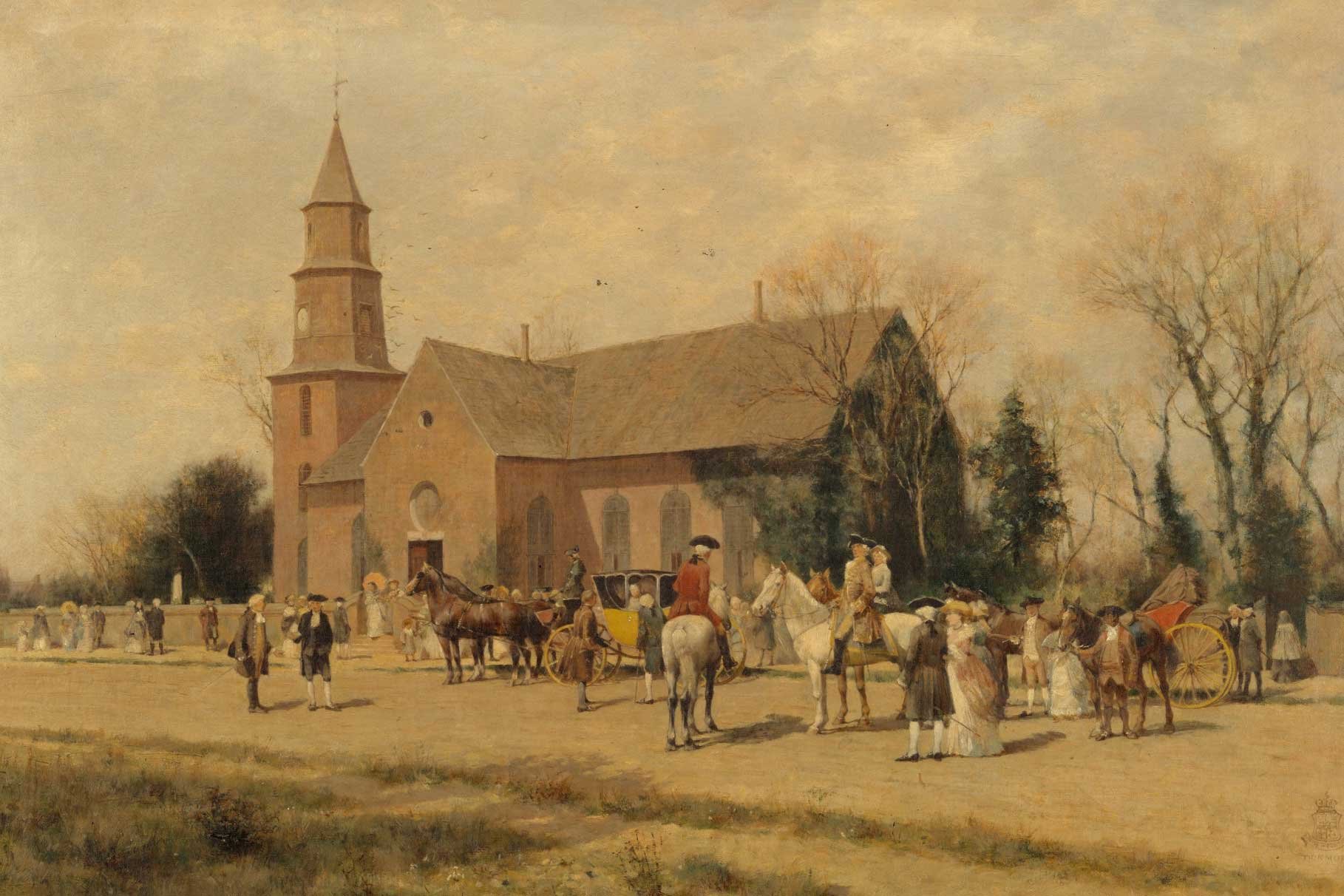
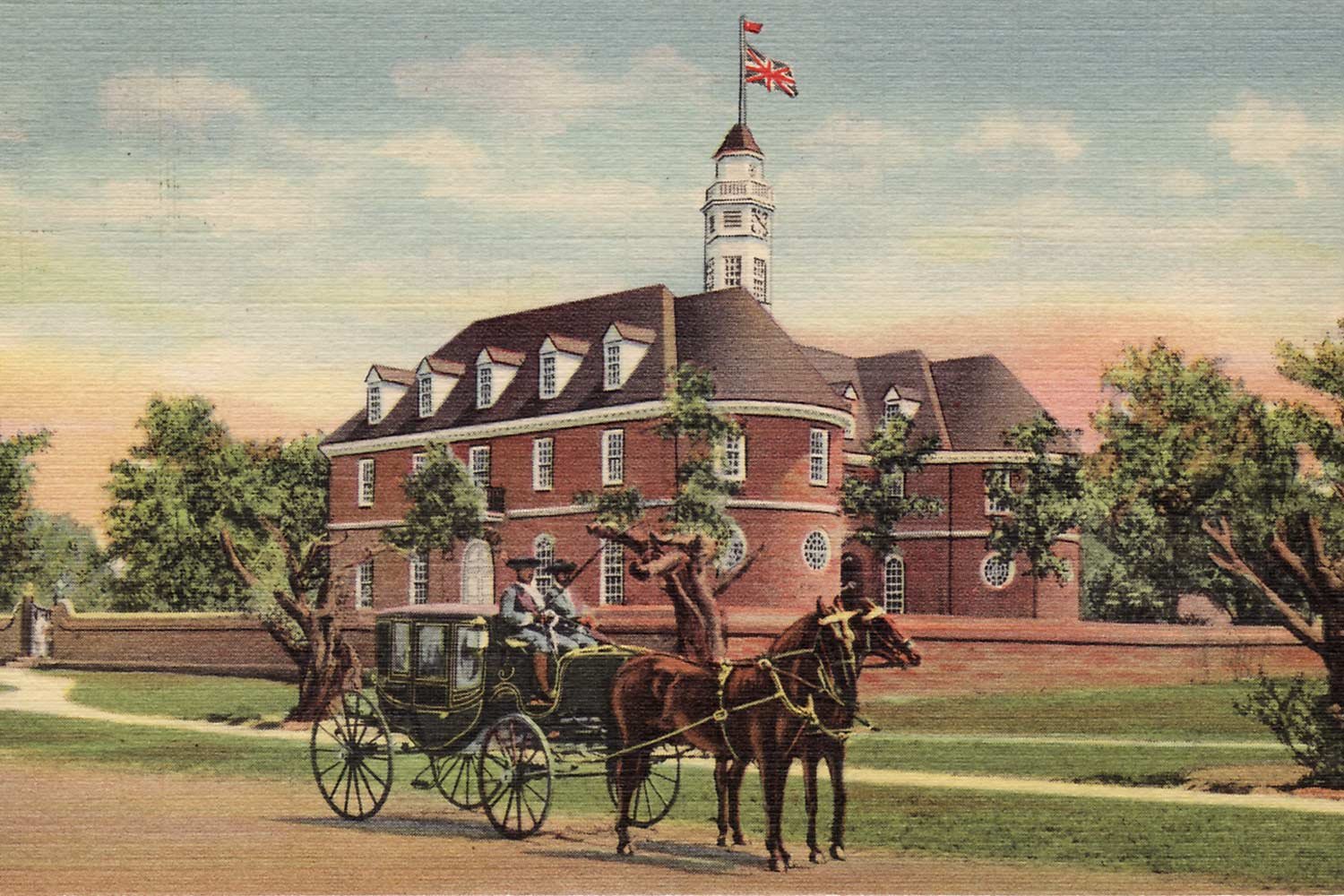
Virginia’s House of Burgesses, British America’s First Elected Legislature
The Colony of Virginia was established at Jamestown by the Virginia Company in 1607 as a for-profit venture by its investors. To bring order to the province, Governor George Yeardley created a one-house or unicameral General Assembly on July 30, 1619.