How Colonial America Was Governed
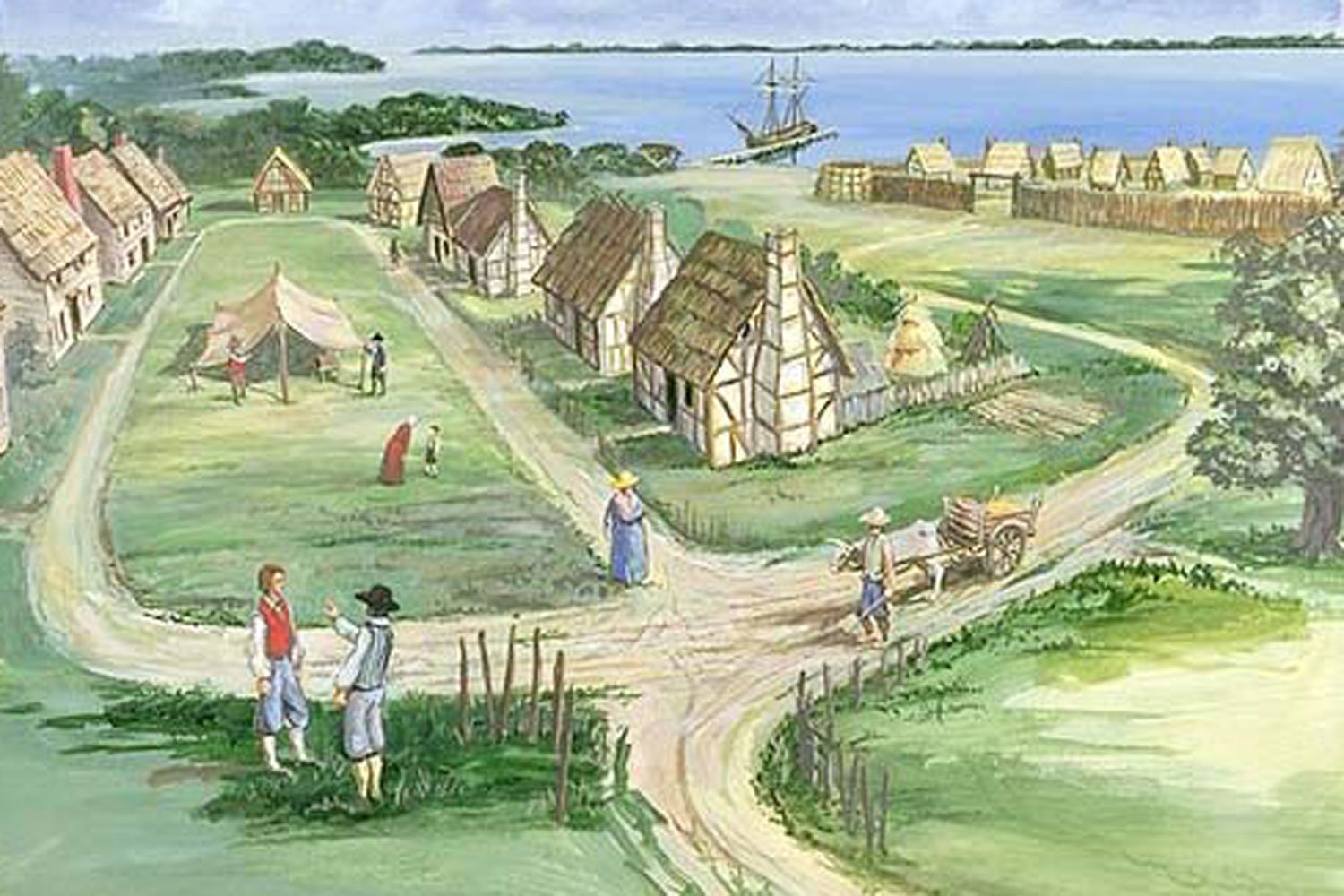
When the English began to settle North America in the 1600's, the leaders of the various colonies had different motives. While all colonies exercised their authority in the King’s name, they were not created in the same mold, and some had more autonomy than others. In fact, there were three different types of colonies: royal, self-governing, and proprietary.
Royal colonies were owned and completely administered by the Crown. The Governor and his Council were appointed by the King and these lands existed simply to generate wealth for England. Although few land grants began as a royal colony, by the American Revolution, eight of the thirteen colonies were this type: Virginia (converted in 1624), New Hampshire (1679), New York (1685), Massachusetts (1691), New Jersey (1702), South Carolina (1719), North Carolina (1729), and Georgia (1753).
Self-governing colonies were formed when the King granted a charter to a joint-stock company which set up its own independent governing system. These organizations were essentially corporations formed to make money for the investors.
Like the entrepreneurs of today, a few men came up with an idea, presented it to their friends and associates, and asked them to invest in their plan. Their organizations had wide latitude to appoint leaders and run their business as they wished. Virginia, Massachusetts Bay, Connecticut, and Rhode Island were all initially established as self-governing colonies.
However, these colonies soon found out that their independence was on a short leash. If the colony was poorly administered like in Virginia or if the people proved troublesome like in Massachusetts, these dominions were converted into a royal colony with all the restrictions that came with it. By the time of the American Revolution, only Rhode Island and Connecticut, retained their original self-governing charter. The King always had the final say.
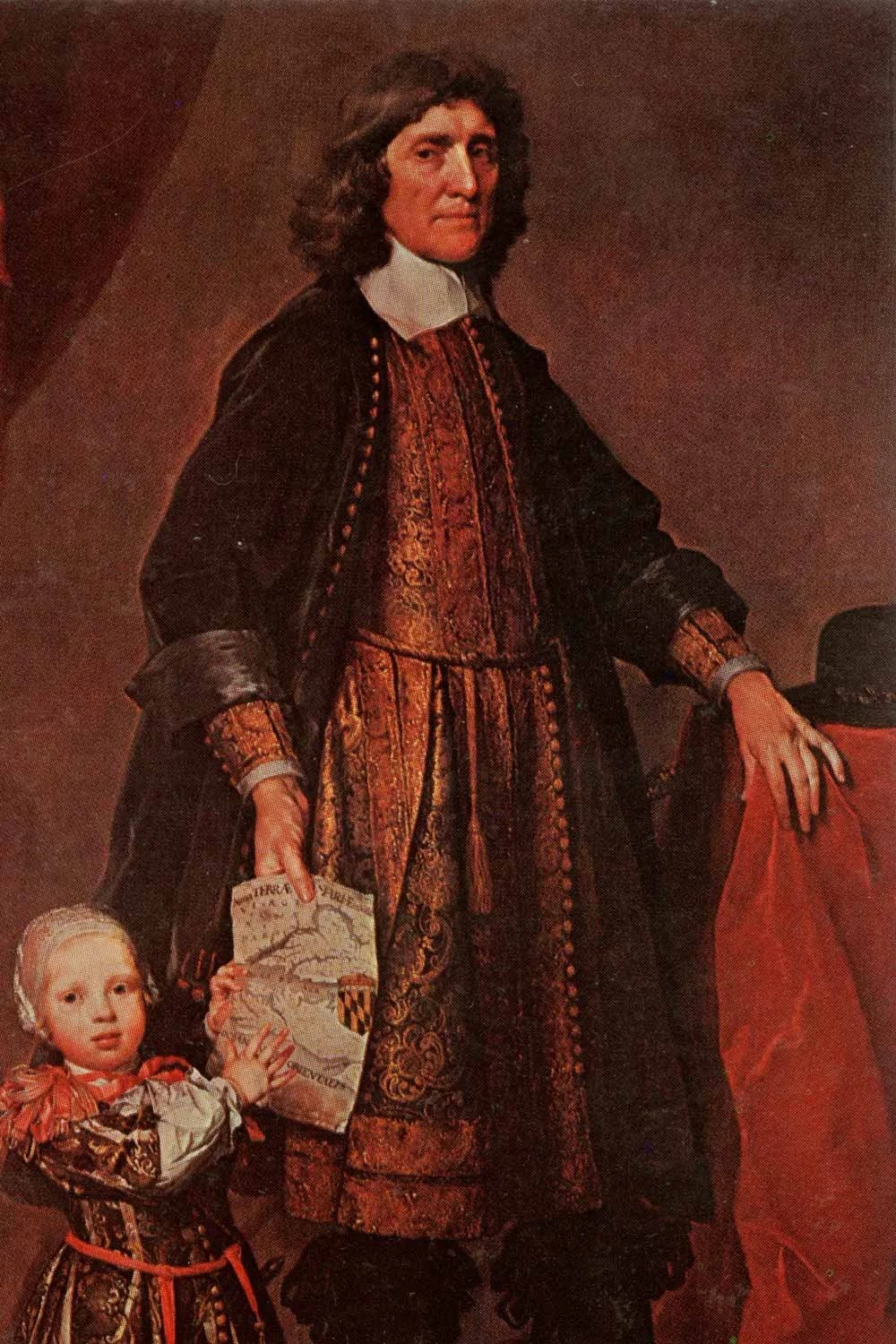
Gerard Soest. “Portrait of Cecil Calvert.” University of Maryland.
Proprietary colonies were land grants given by the King to one or a few favored men called proprietors. They in turn were to administer these areas for the Crown but in a manner to be determined by them. The proprietors appointed the Governor and his Council, determined the laws (but they had to be approved by the Crown), and ran the territory as they saw fit. While the King had the ultimate authority, the rule of the proprietors resembled that of a monarch.
Maryland was an example of a proprietary colony. It was established by Cecil Calvert in 1632 upon receiving a land grant from King Charles I. Lord Calvert, also known as the 2nd Baron Baltimore, wanted to develop a land where Catholics could openly profess their faith without fear of retribution.
After several starts and stops, settlers for this new colony finally arrived in 1634. The colony prospered and in 1649 Maryland passed the Maryland Toleration Act, the first law establishing religious tolerance in British North America. Although Lord Calvert never visited Maryland, the Calvert family managed the province well and never had their charter revoked.
Not surprisingly, these proprietary colonies which operated without a great deal of input from England, were not as anxious to sever ties with the Mother Country as those with more stringent controls. For example, the Pennsylvania Assembly had to replace five of its initial nine delegates to the Second Continental Congress to get a majority of delegates to be in favor of independence.
Delaware, which was another proprietary colony, had to send an extra delegate, Caesar Rodney, on a midnight 80-mile ride to Philadelphia to break the tie in their delegation so the state could vote for independence. By the time of the American Revolution, only Delaware, Maryland and Pennsylvania remained as proprietary colonies, none of which were hot beds of rebellion.
WHY IT MATTERS
So why should the way in which colonies were organized and governed matter to us today? The three types of colonies with their different systems of government generated varying attitudes towards English rule and our independence. Understanding these conflicting feelings helps us to better appreciate why not all Americans wanted to break from the Mother Country.
What we see is that those colonies left to govern themselves were fairly content living under English rule and not as anxious to break from England. In retrospect, England may have been wiser to allow all the colonies to operate with more autonomy and to manage them in a less oppressive manner.
SUGGESTED READING
If you are interested in a deeper dive into this subject, Colonial America: A History to 1763 is an excellent book on background, founding, and development of the thirteen British North American colonies. It was written by Richard Middleton and Anne Lombard and originally published in 1992, but it was updated in 2011.
PLACES TO VISIT
The statehouse in Annapolis, Maryland is an incredibly beautiful building and a great example of architecture from our colonial era. It is the oldest state capital in continuous legislative use and is the only statehouse ever used as the nation’s capital. Seeing it and the rest of this historically significant seaside city would be well worth your time.
Until next time, may your motto be “Ducit Amor Patriae”, Love of country leads me.











The midnight deal Robert Livingston, United States Minister to France, struck with Francois Barbe-Marbois, Napoleon’s Finance Minister, on April 13, 1803, to purchase the Louisiana territory was one of the most impactful agreements in the history of the United States. It resulted from months of conversations Livingston had had with numerous French officials, creating a foundation for the details that would follow. But as important as this step was, there remained several hurdles to overcome.