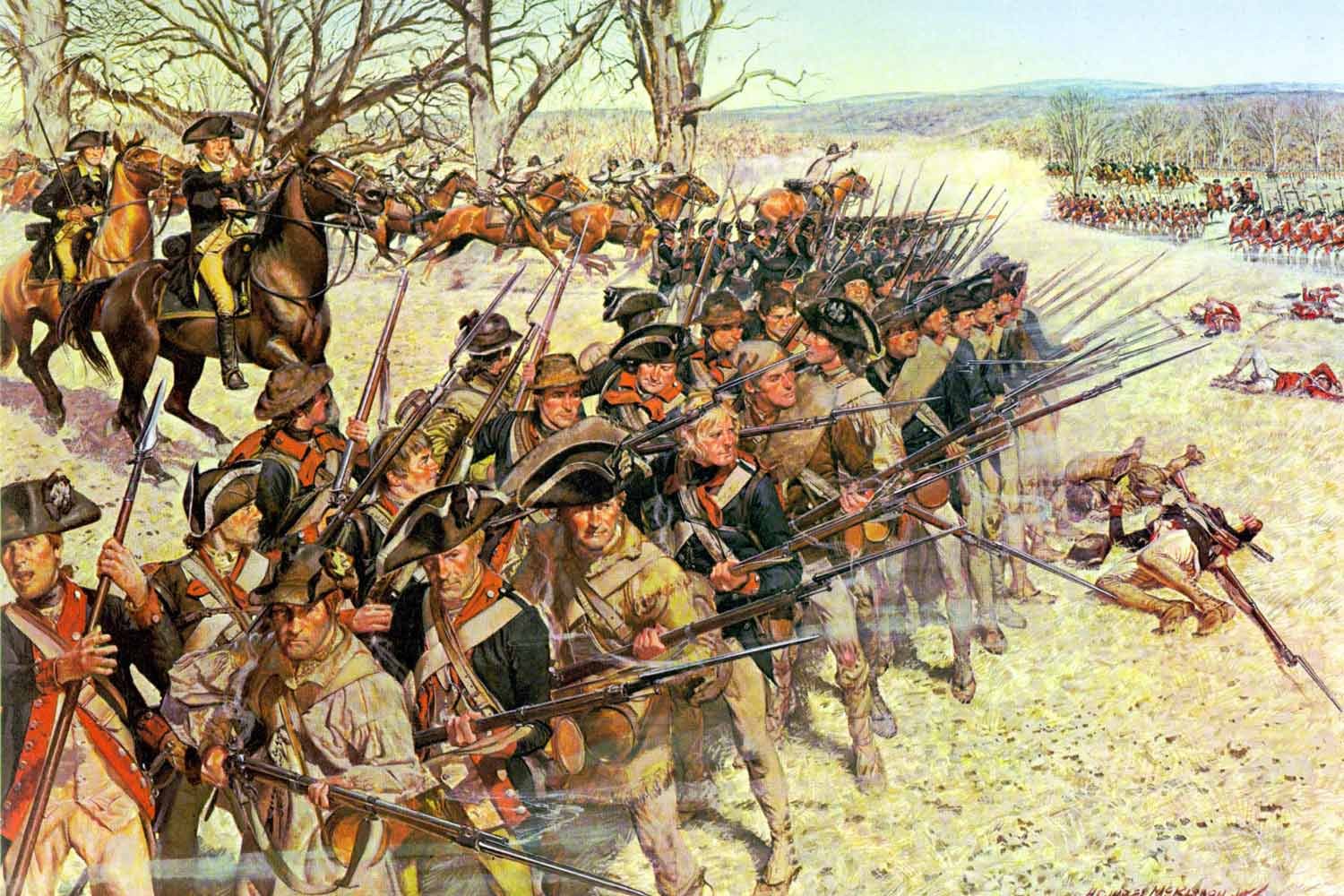


The Battle of Guilford Courthouse
Following the successful conclusion of the Race to the Dan, General Nathanael Greene and his southern army was safe for the moment from the British troops under Lord Charles Cornwallis just across the river. Due to a lack of supplies in the area, Cornwallis retreated to Hillsboro, about sixty miles southeast, to get refitted. By late February, Greene had received reinforcements, recrossed the Dan, and had the American army back in North Carolina.
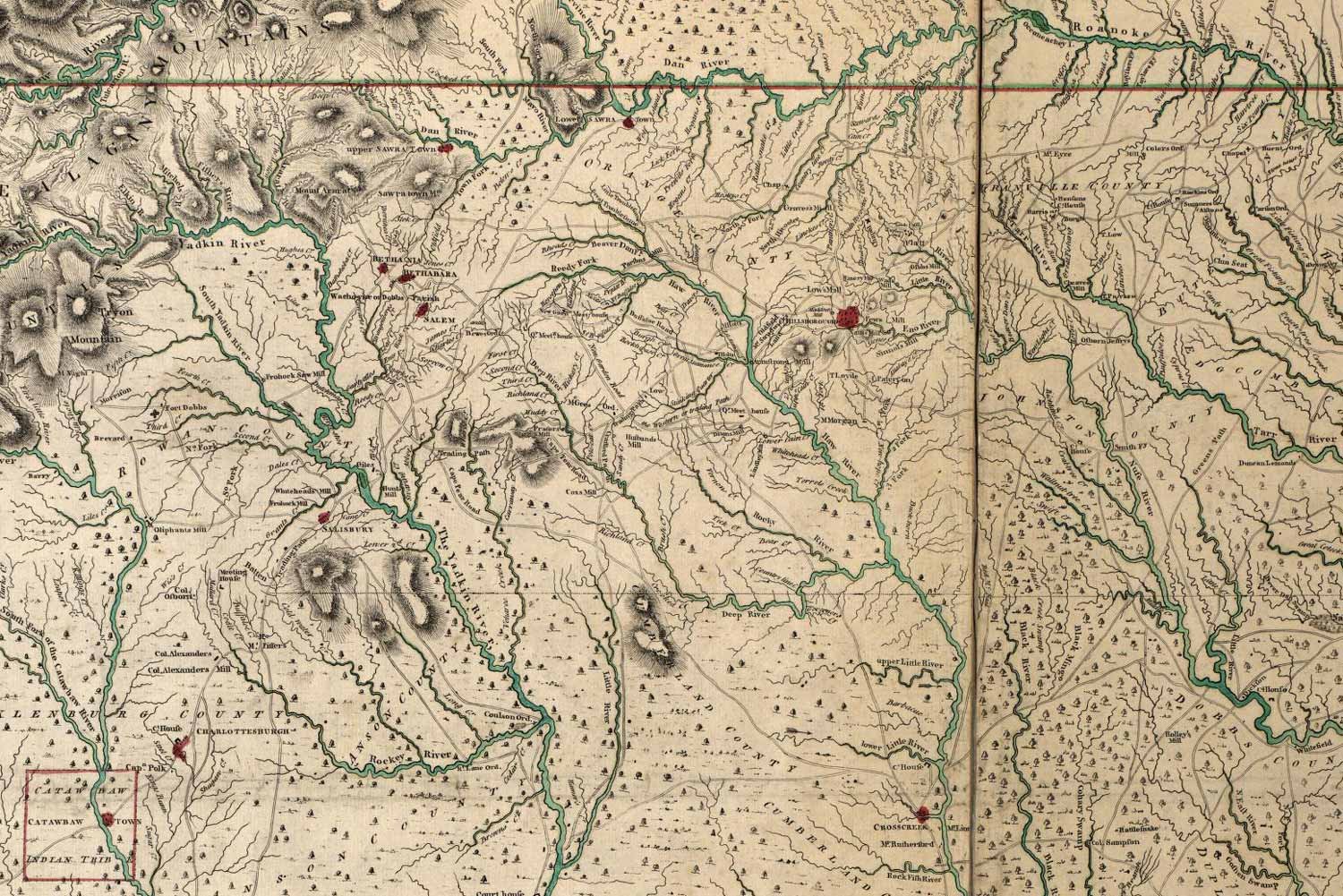
The Race to the Dan
The Battle of Cowpens on January 17, 1781, was a great victory for Daniel Morgan and his army of Continentals and militiamen. They had virtually annihilated Lieutenant Colonel Banastre Tarleton’s famed British Legion, but Morgan’s contingent was in a dangerous position, with a larger British force under Lord Charles Cornwallis only twenty-five miles away. The race was now on to get to a place of safety.
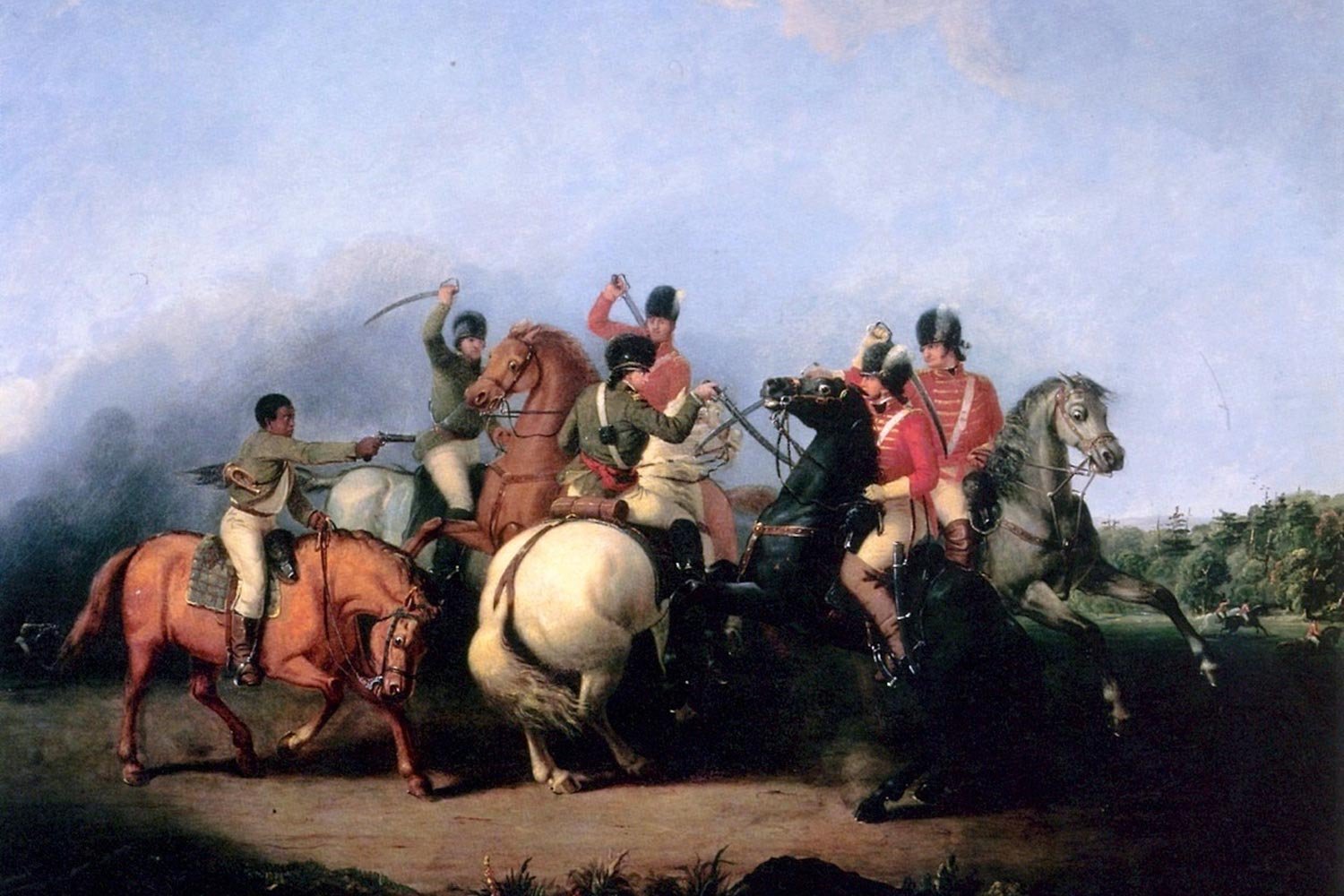

Daniel Morgan’s Masterpiece at Cowpens
Daniel Morgan came out of his self-imposed retirement and returned to the Continental Army near Hillsborough, North Carolina in late September 1780. He felt he could no longer sit on the sidelines while his country was at war. In December, Major General Nathanael Greene sent newly promoted Brigadier General Morgan and 600 men west to threaten British outposts in western SC.
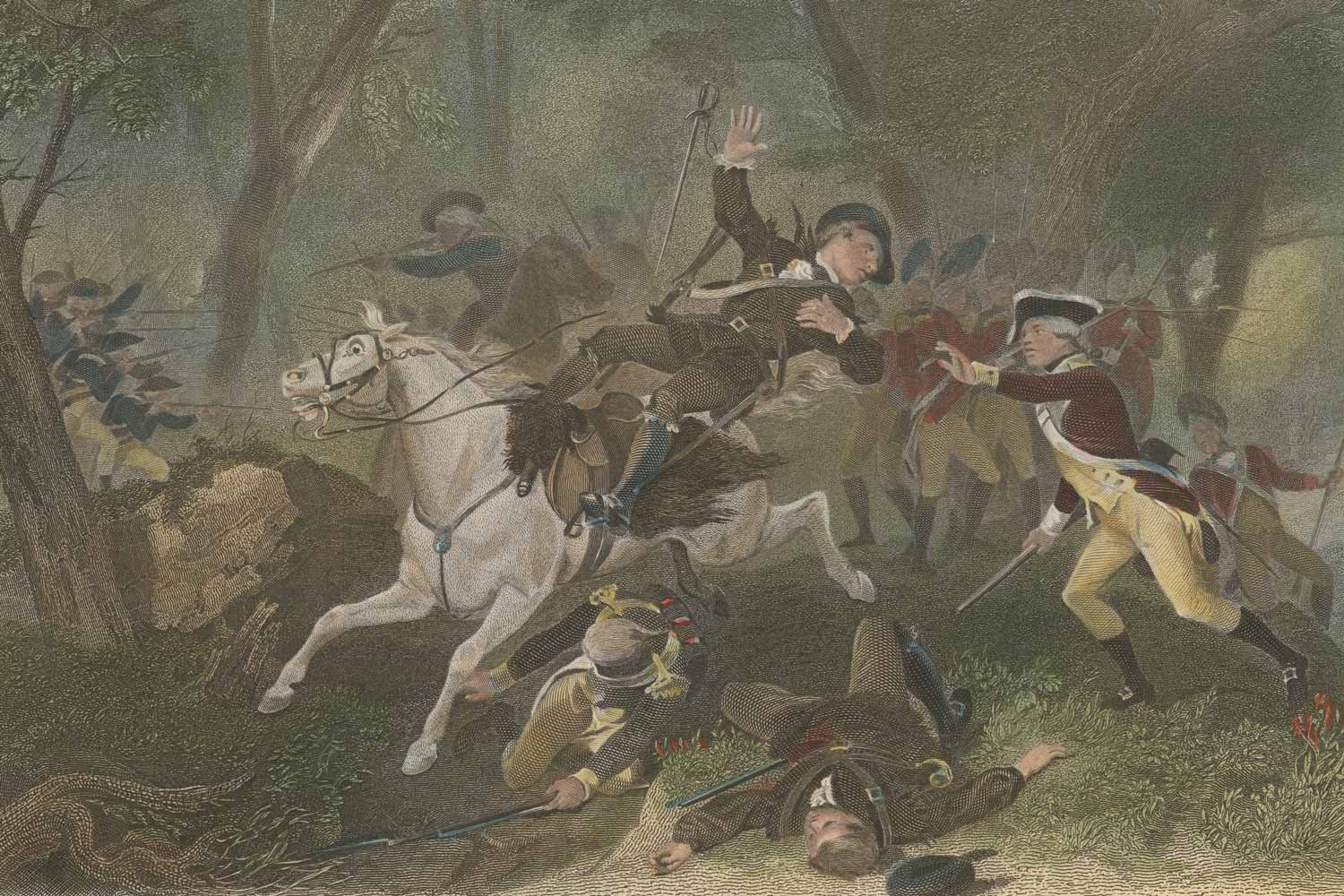

American Victory at King’s Mountain
In July 1780, Patriot partisan bands in the backcountry of South Carolina launched a series of successful attacks on Loyalist contingents, weakening the British hold on the state. These rapid-fire engagements continued into August as six more Patriot partisan victories were sandwiched around the disastrous Continental Army defeat at Camden and the capture of an American supply train at Fishing Creek.
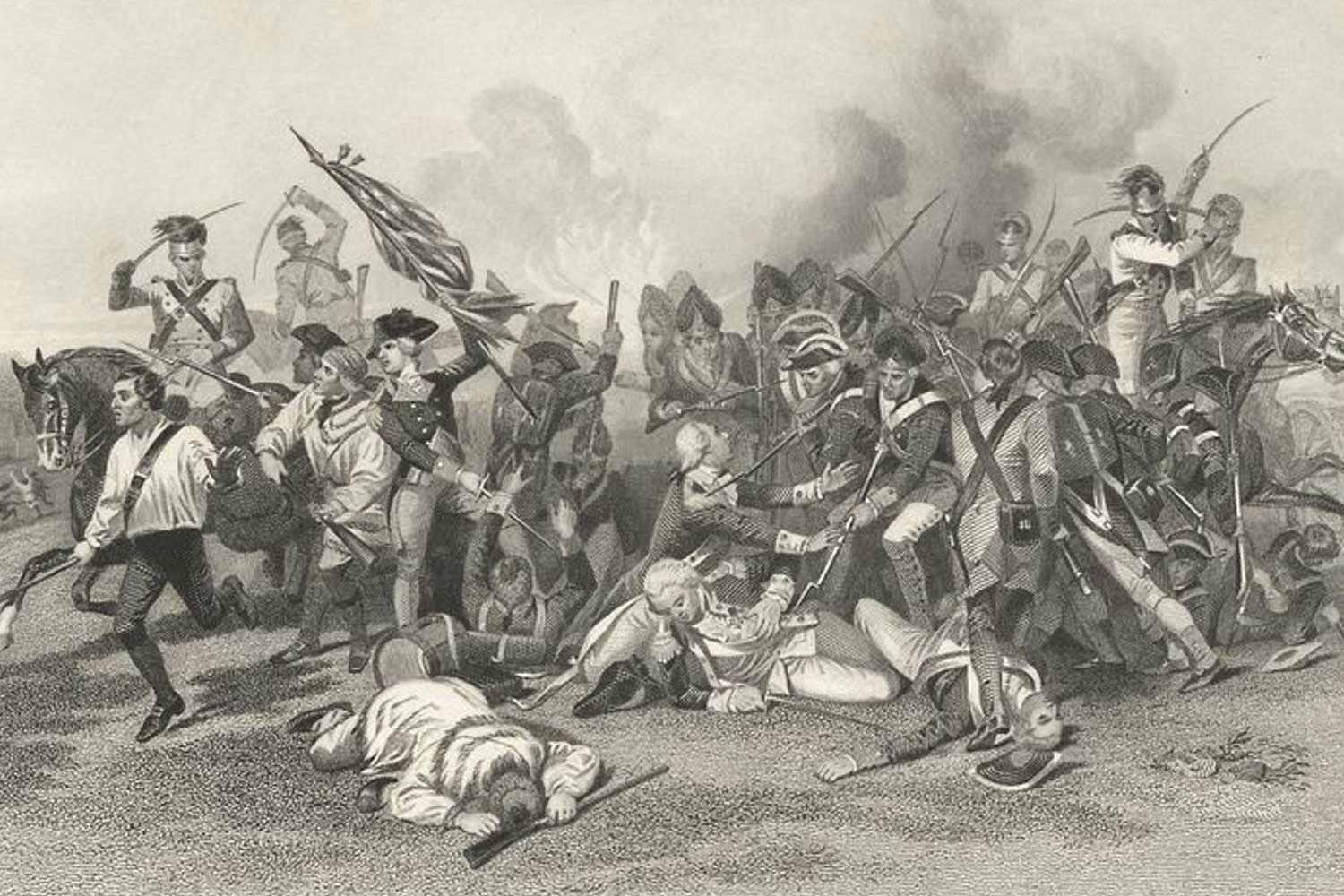

British High Tide at Camden
As dawn broke on the morning of August 16, 1780, the British army under Lord Charles Cornwallis and the American southern army under Major General Horatio Gates were half a mile apart, preparing to do battle. It would be a short affair, but a costly one for the Americans.
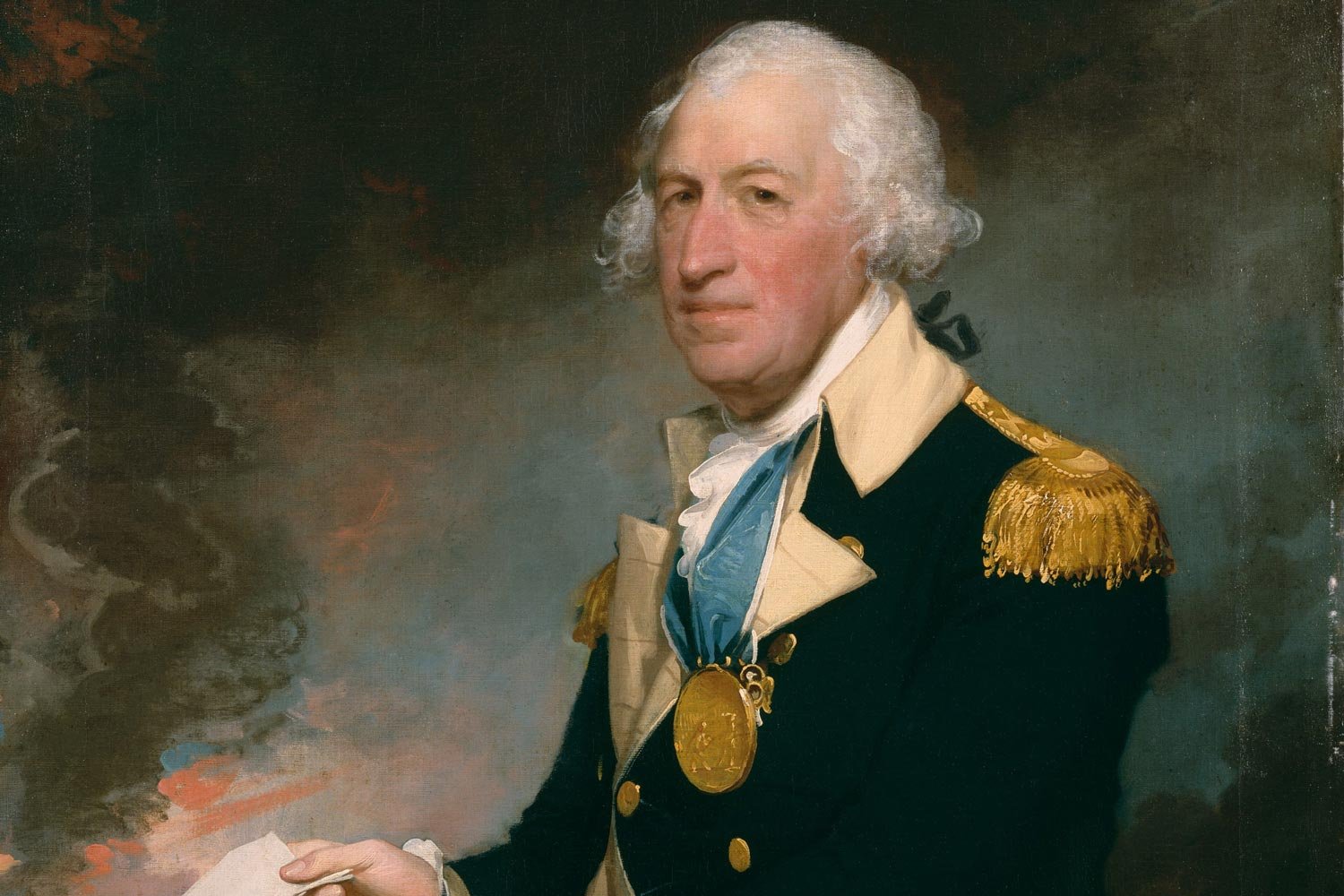

Southern Continental Army Tries to Regroup Under General Gates
The surrender of Charleston and its entire 5,000-man garrison on May 12, 1780, essentially eliminated the American southern Continental Army. At that point, Lord Charles Cornwallis and his British legions were able to operate virtually unopposed in South Carolina.

Patriots Turn the Tide in South Carolina’s Backcountry
For the first five years of the American Revolution, the deep southern states of Georgia and the two Carolinas were mostly observers of the conflict. Other than a failed attempt to take Charleston in 1776 and the capture of Savannah in December 1778, the British had focused their efforts in the north.
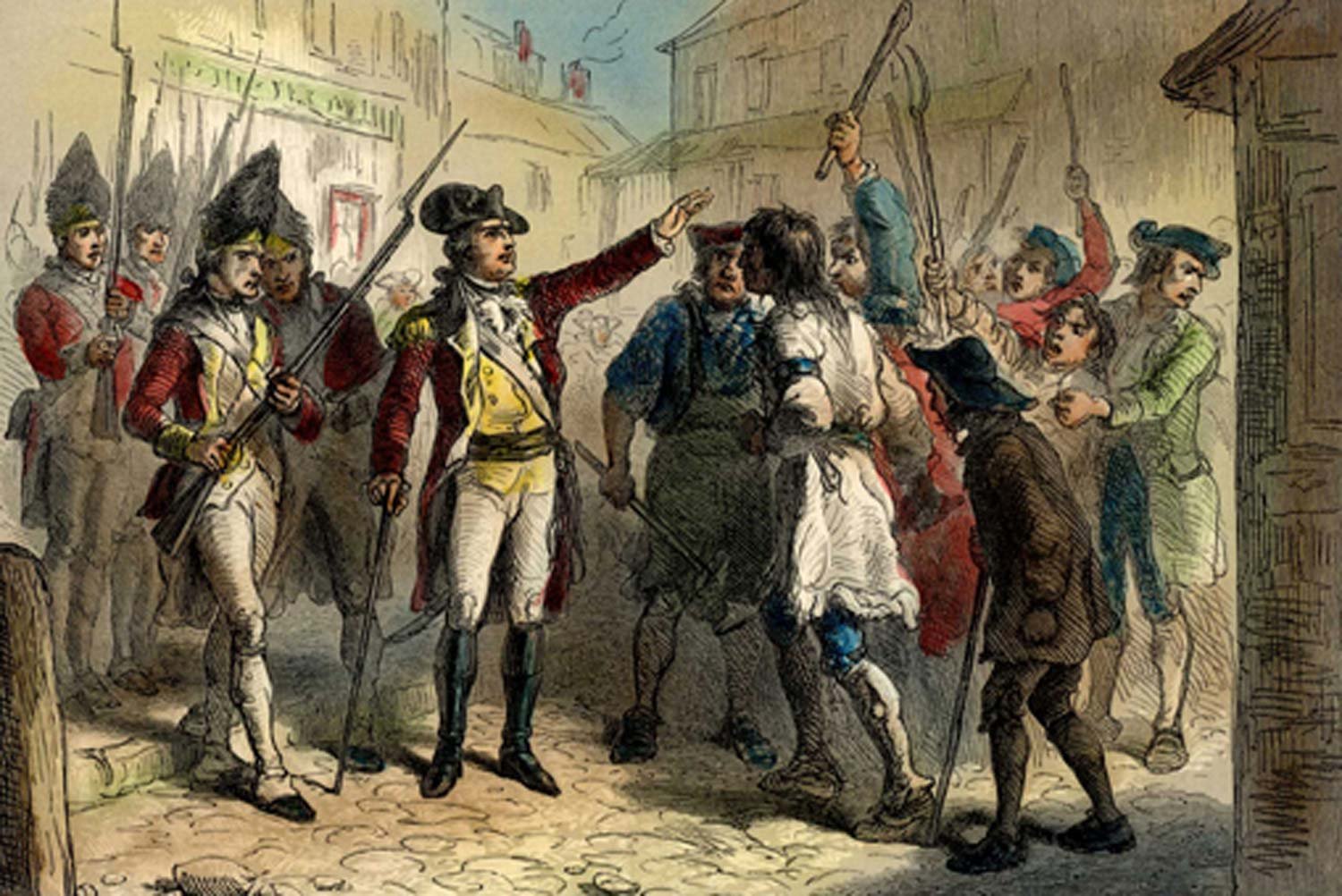

North Carolina’s Regulator Insurrection
The first time a Royal Governor of a British American colony called out the troops to suppress rebellious American subjects was not the famous fight at Lexington and Concord in 1775. The initial incident of this sort occurred four years earlier when the Royal Governor of North Carolina, William Tryon, suppressed a grassroots effort known as the Regulator Insurrection.

History of the South Carolina Backcountry
Following General Benjamin Lincoln’s surrender of Charleston on May 12, 1780, Sir Henry Clinton, the British commander, offered a full parole to the captured Americans as long as they remained neutral. The other American garrisons in the state at Ninety Six, Camden, Beaufort, and Georgetown were extended these same terms.
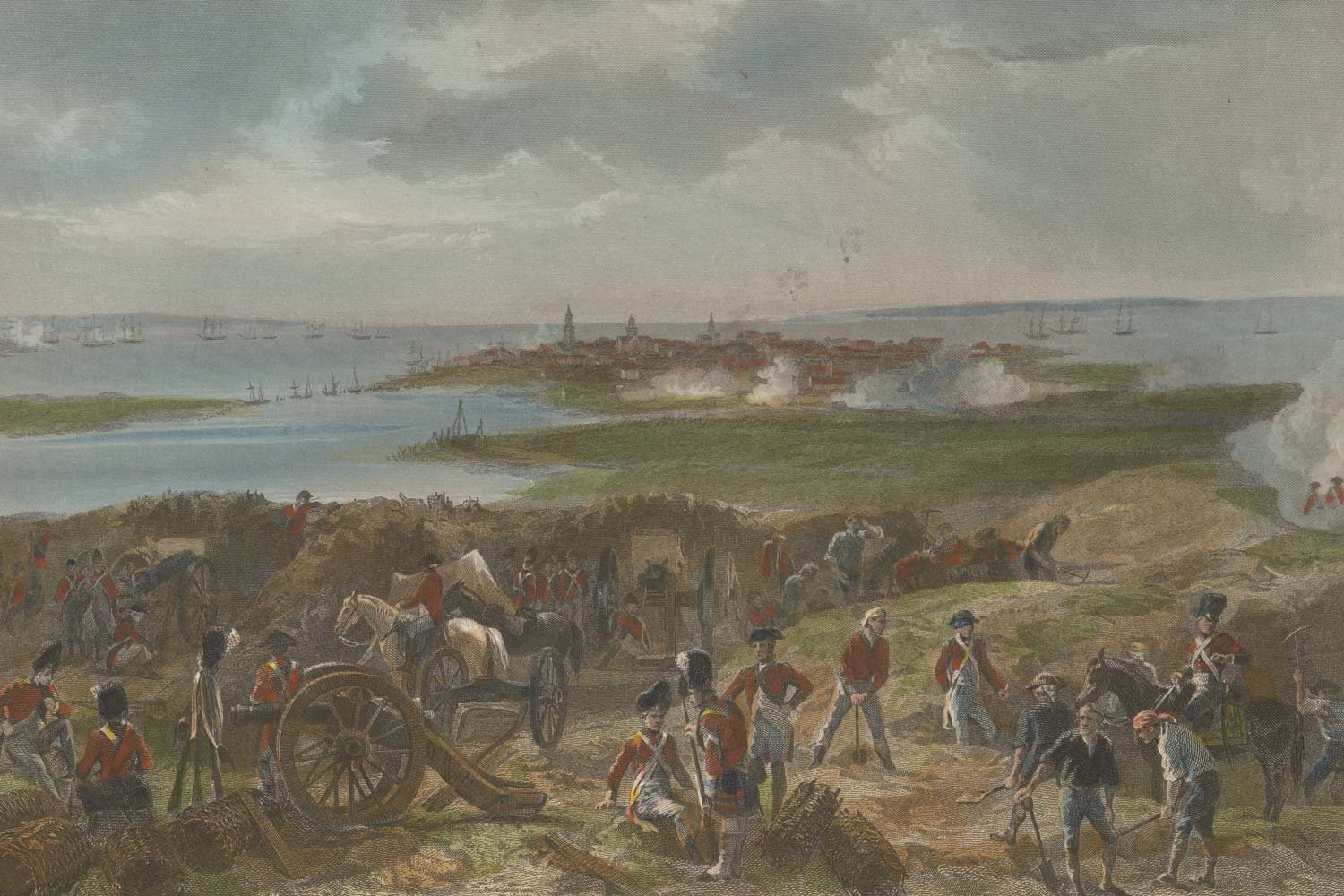

Charleston Surrenders to British
Following the fall of Savannah in 1778 and the subsequent failed American French effort to recapture it in October 1779, Sir Henry Clinton, the commander of British forces in North America, set his sights on the South Carolina port city of Charleston.
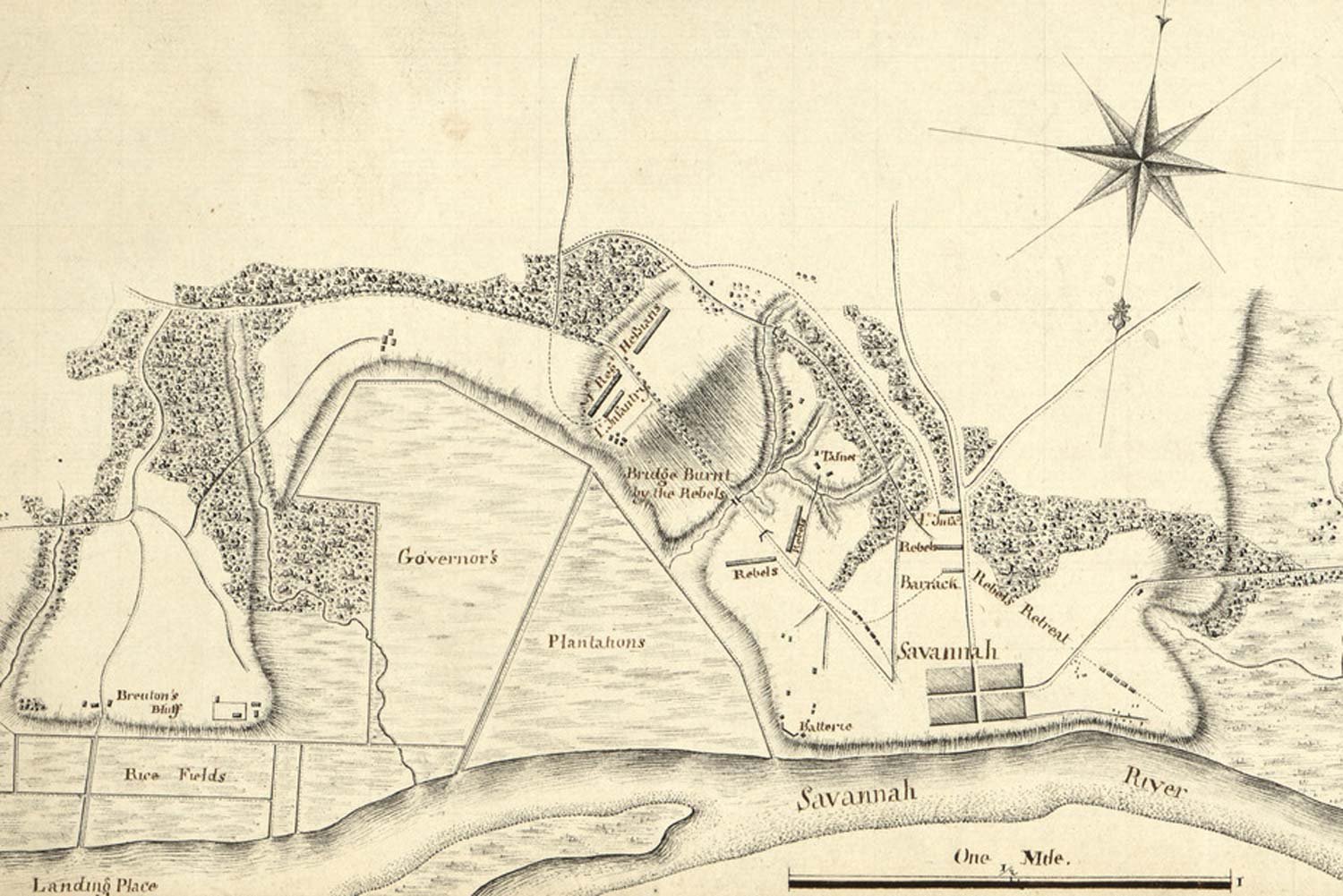
British Capture Savannah
In 1778, after three years of fighting their rebellious American colonists, the grand British Army was largely confined to New York City and Newport, Rhode Island. General George Washington’s Continental Army controlled virtually everything else as the hoped for Loyalist uprising in rural colonial America had failed to materialize. During this period, the British had focused their efforts on the northern colonies, basically from Pennsylvania north to New York, New England, and the Canadian border.
End of the Mohawk Valley War
By the spring of 1780, the bloody civil war in the Mohawk Valley had been raging for four long years. The suffering in the region was universal, having affected Loyalists, Patriots, and the Iroquois Confederacy. Despite the punitive Sullivan Expedition in the fall of 1779 which laid waste to the heart of the Iroquois homeland, the Loyalists and Indians were not vanquished.




