
Thomas Jefferson’s “Summary View”
Thomas Jefferson’s revolutionary journey began in the 1760s and culminated in his masterfully written Declaration of Independence in 1776. But in between these events, Jefferson crafted one of the most impactful statements ever for American independence. Entitled A Summary View of the Rights of British America, it was perhaps the most logical assessment of the true relationship between Great Britain and her American colonies. The concepts Jefferson laid out had been refined and brought into focus following several dustups with Lord Dunmore, the new Royal Governor.

Thomas Jefferson, the Virginia Barrister
In 1765, Parliament passed the Stamp Act, the first internal tax on the American colonies, and thus began a decade of missteps by the British. Their miscalculations would take their country and their colonists on a direct path to Lexington Green and Concord Bridge on April 19, 1775. During this same year, Thomas Jefferson was concluding his time studying law under George Wythe and began to turn his eye towards the world at large and, more specifically, politics in the Colony of Virginia.

The Early Life of Thomas Jefferson
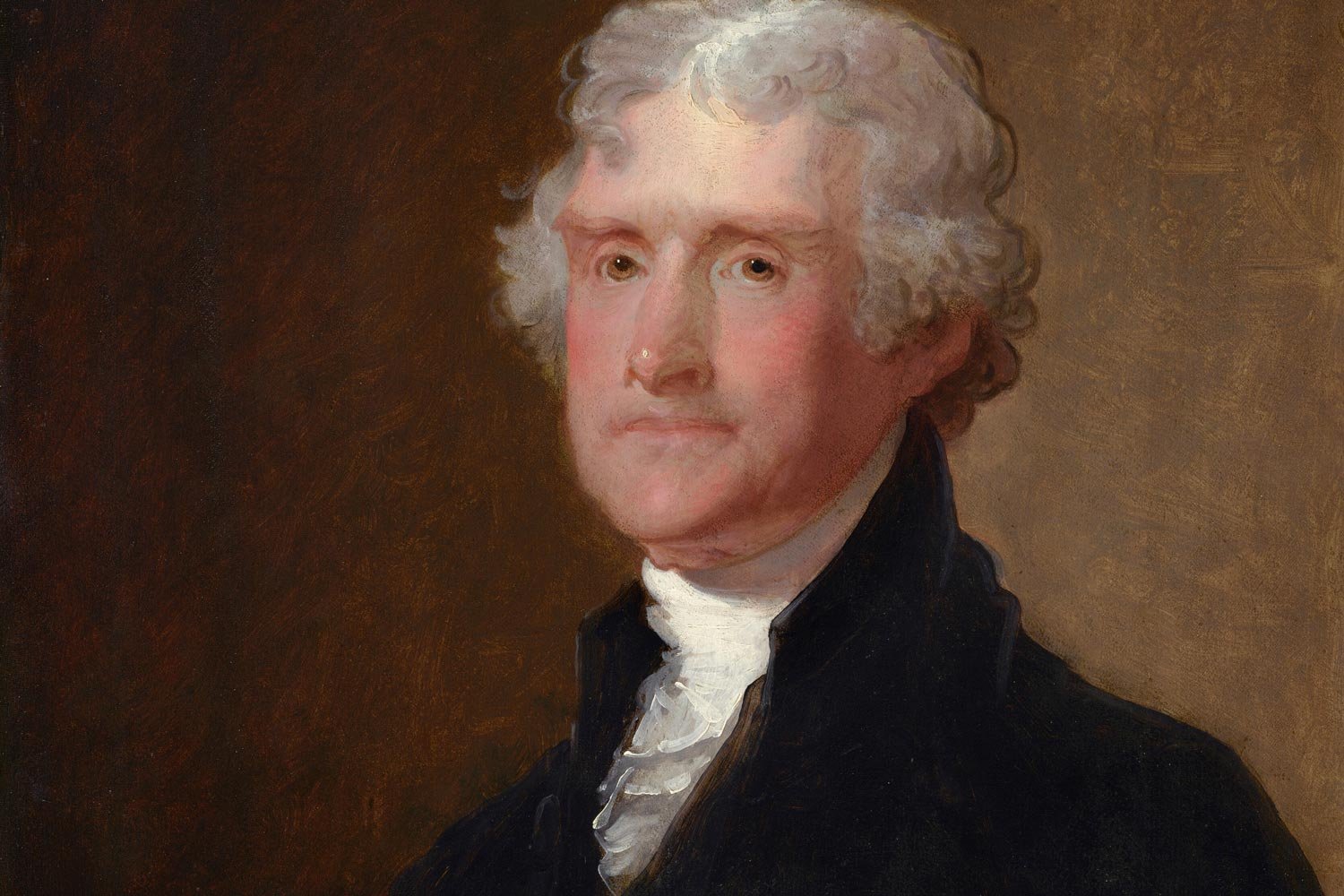
Thomas Jefferson is one of America’s most iconic Founding Fathers. Best known for his inspirational words in the Declaration of Independence, Jefferson was a brilliant man with diverse interests who spent the bulk of his life in service to his country and his later years in retirement at his beloved mountain home of Monticello, near Charlottesville, Virginia.

The House of Representatives Chooses Thomas Jefferson
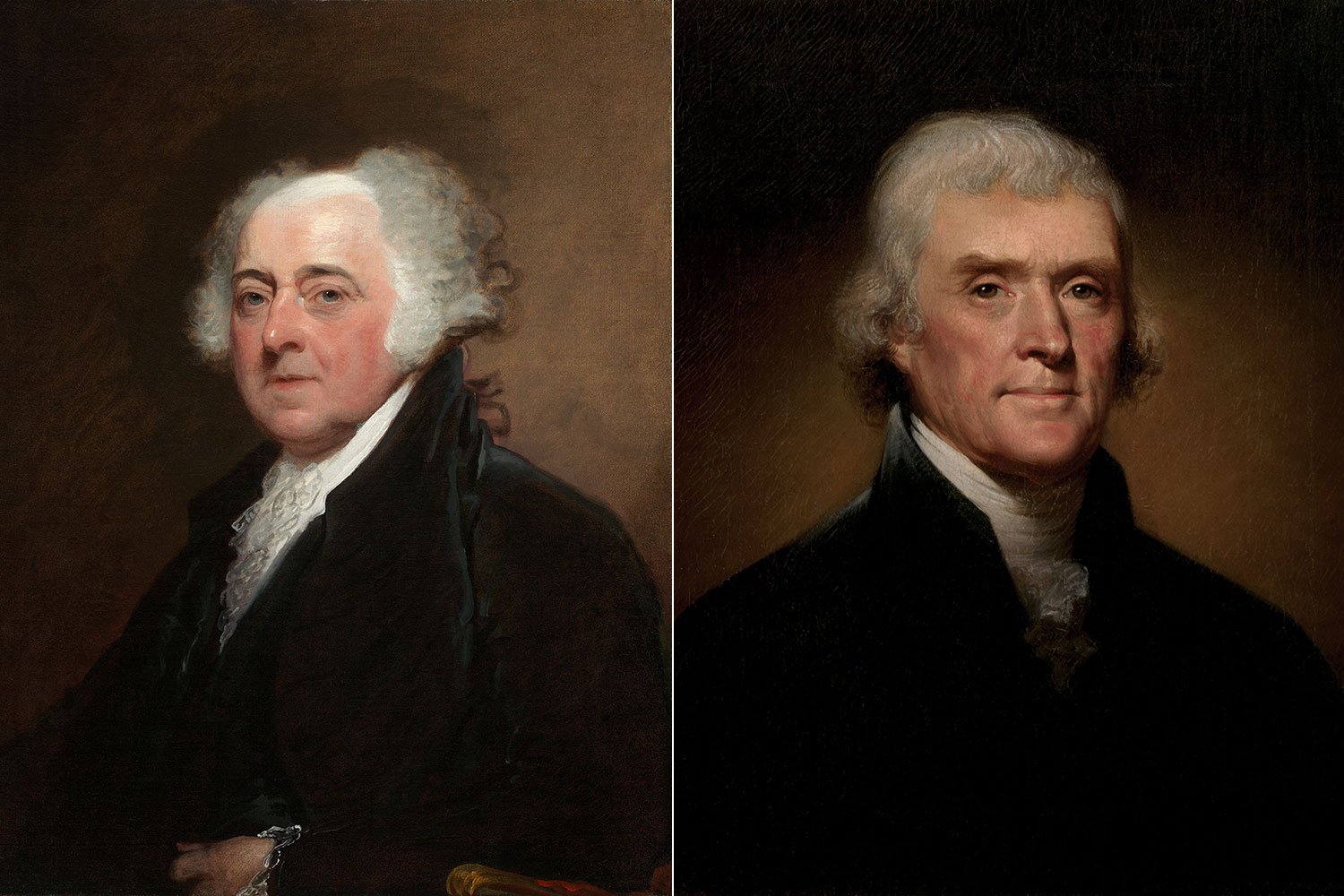
The presidential election of 1800 ended in a tie, as the two Democratic-Republican candidates, Thomas Jefferson and Aaron Burr, each received 73 electoral votes under the original guidelines of the Constitution.

The Election of 1800
The Presidential election of 1800 was one of the most controversial and consequential in the history of the United States. It represented a true changing of the guard as the Federalist party of Washington, Hamilton, and Adams gave way to the Democratic-Republican ideals of Jefferson and Madison and took the United States in a different direction for a generation to come.

The Legacy of John Adams
John Adams’s loss to Thomas Jefferson in the presidential election of 1800 was a great disappointment for Adams as he felt he deserved another term based on his accomplishments during his four years as President. But Adams accepted the verdict of the Electoral College and looked forward to the next phase of his life.

The Election of 1796
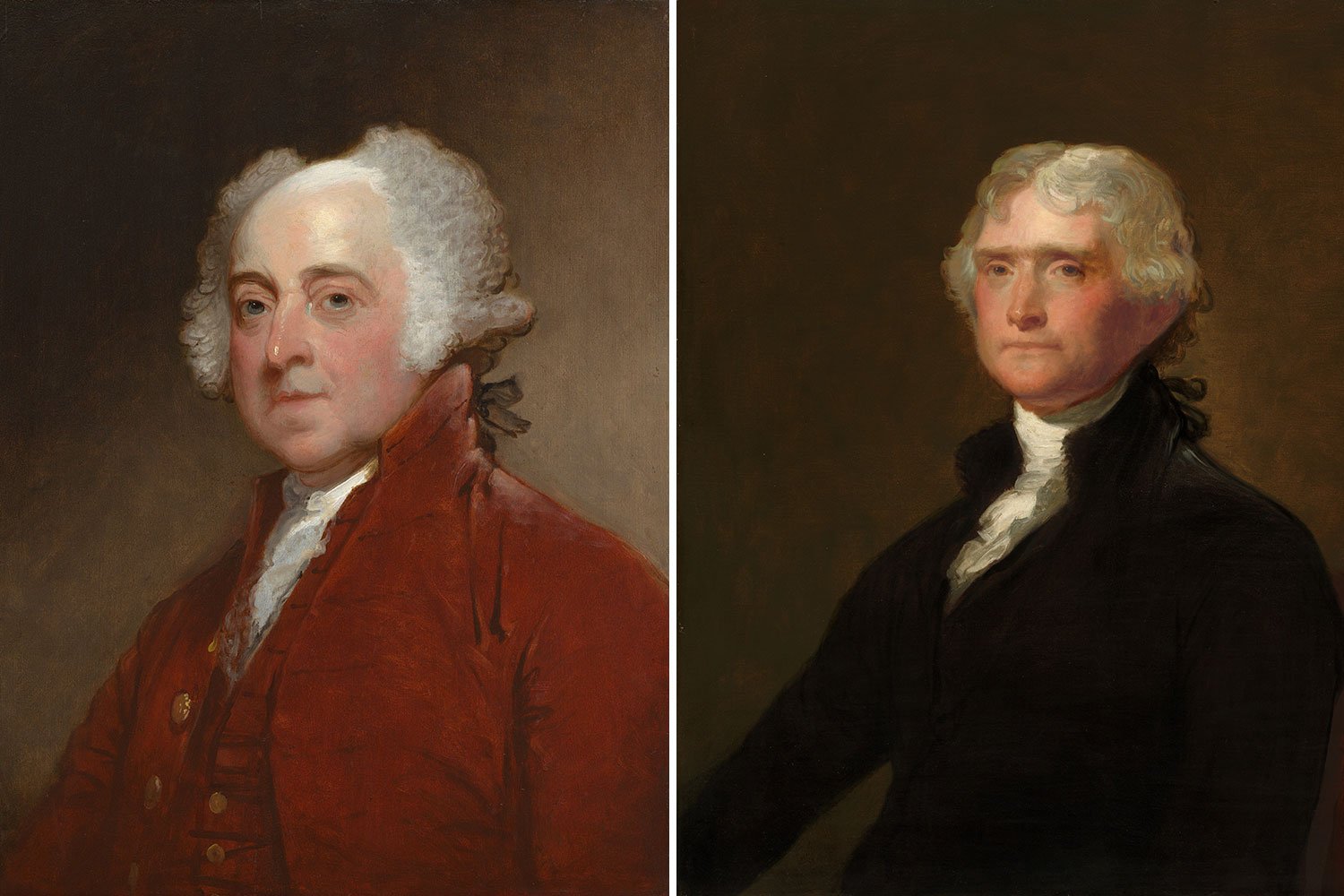
After serving two terms as President, George Washington decided to not seek a third and instead retire from public life. His decision led to the country’s first contested presidential election in the fall of 1796, pitting Thomas Jefferson against Vice President John Adams. Arguably, no presidential election in the history of the United States has ever featured a choice between two such American titans.
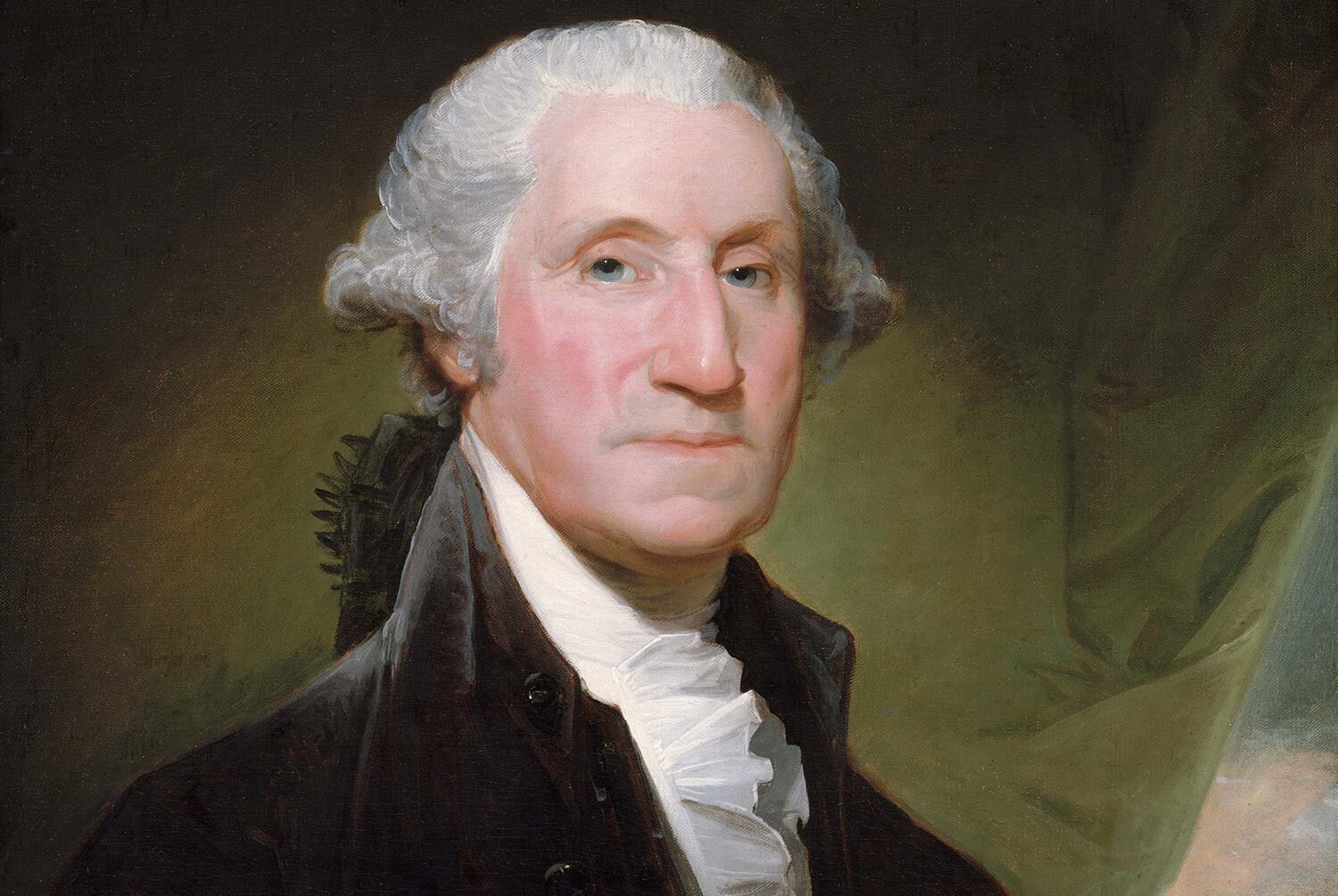

George Washington, Our Nation’s First President
The federal Constitution, the new law of the land, took effect on March 4, 1789, and had several notable differences with the Articles of Confederation. One of the most significant changes was the creation of a strong executive or President. However, the powerful executive reminded skeptics of the authority held by King George, and they worried the United States could eventually drift towards despotism. Virtually everyone knew that the only man strong enough to lead the nation and conscientious enough to be entrusted with so much power was George Washington.

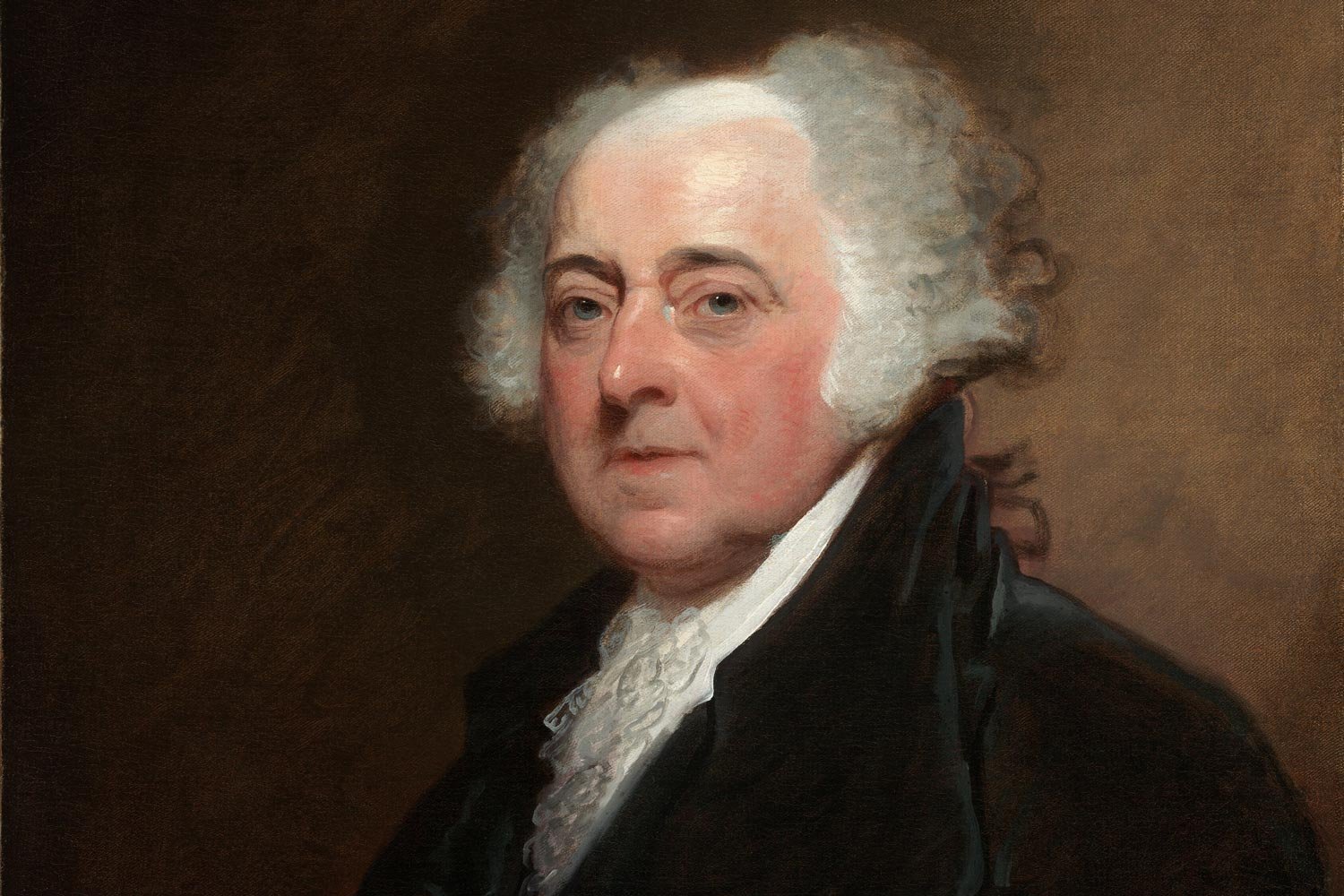
The Inspiring Legacy of John Adams
John Adams lost the Presidential election of 1800 to Thomas Jefferson after a bitter fight. Adams was terribly disappointed as felt he deserved another term, but he accepted the verdict of the Electoral College.
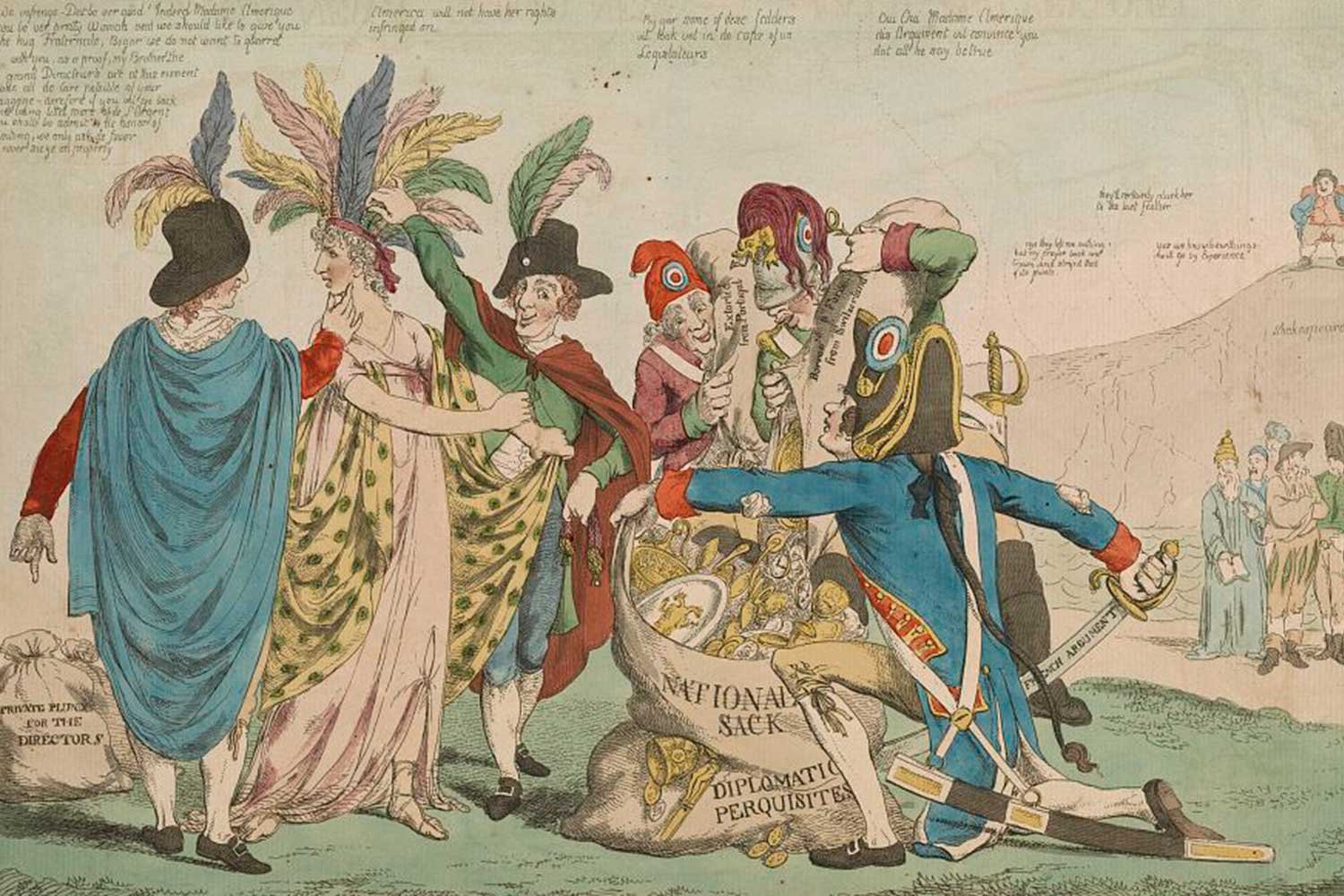

The Presidency of John Adams
To avoid a war with France, in 1797, President John Adams sent a diplomatic delegation to Paris to calm rising tensions. When our team arrived in France in October 1797, they were approached by three French officials whose code-names were X, Y, and Z. These Frenchmen demanded large bribes from the Americans for themselves and other French officials before negotiations could start.

John Adams and the Presidential Election of 1796
After eight years as Vice President under George Washington, John Adams hoped to succeed the Father of our Country as President of the United States. His successful election in 1796 gave him his chance.
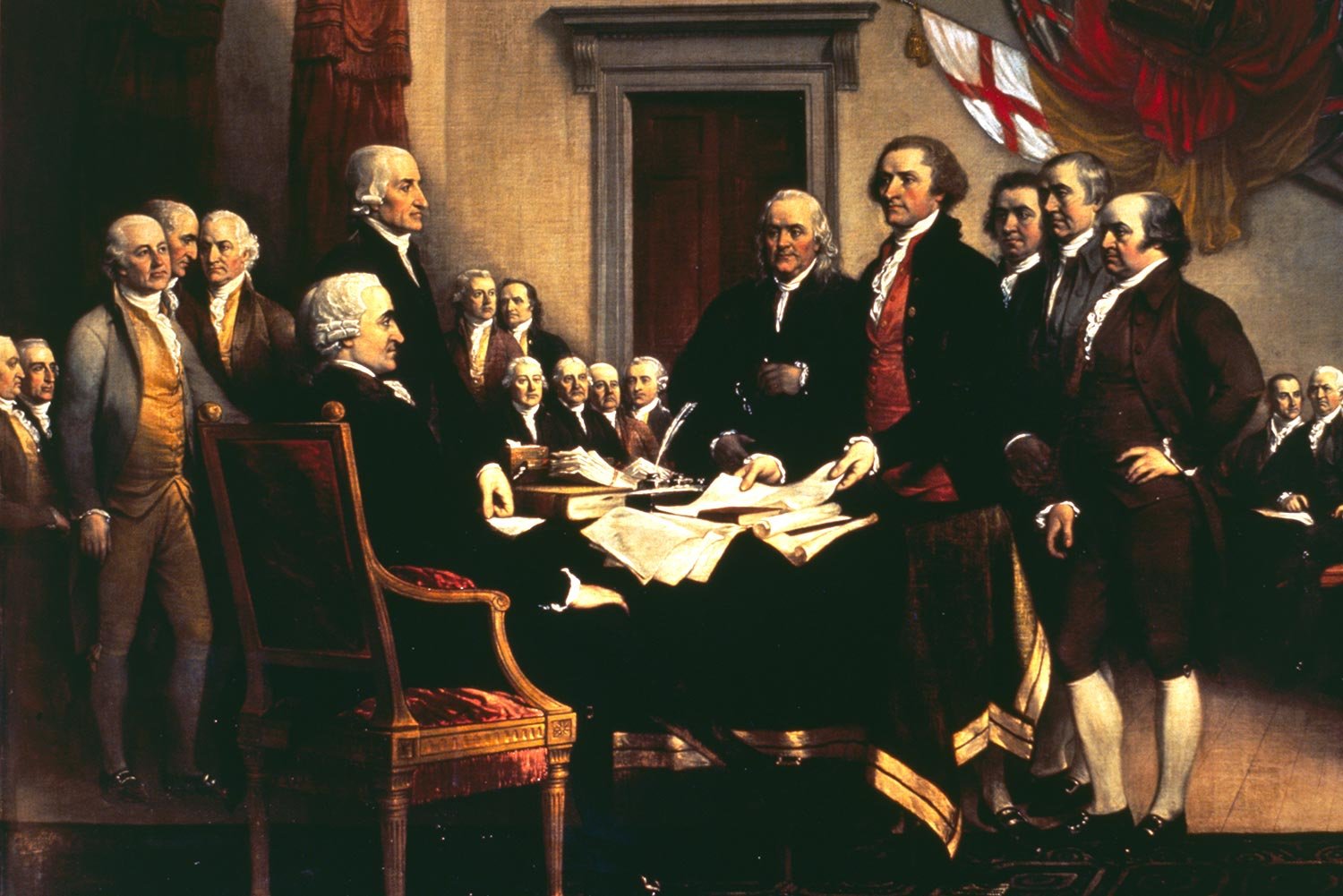

John Adams Dominates Second Continental Congress
John Adams dominated the Second Continental Congress like no other man and was tireless in his efforts to move the assembly towards independence. He sat on ninety committees and chaired twenty-five of them. No other delegate matched his workload.




